JPA Test
JPA Test
Flow
- Application init
- Create
EntityManagerFactoryper database EntityManagerFactorycreatesEntityManagerper user request- Close
EntityManageron end of request- Return DB connection pool on close
- Close
EntityManagerFactoryon end of WAS
Persistence Context
https://docs.oracle.com/javaee/7/api/javax/persistence/EntityManager.html
EntityManager인스턴스는Persistence Context와 연관되어있습니다.Persistence Context는, 모든 영속 entity id 마다, 고유한 entity 인스턴스를 가지는, 인스턴스 집합입니다.Persistence context안에서 entity 인스턴스들과 그들의 lifecylce은 관리됩니다.EntityManager API는 영속된 entity 인스턴스를 생성, 그리고 제거하고, 그들의 primary key를 사용하여 탐색하며, entity들을 통한 질의를 하는데 사용됩니다.
Persistence Context는 모든 고유한 Entity를 저장 및 관리하는 환경입니다.
하지만 실제 구현제가 있는 것은 아니고 논리적인 개념으로써 존재합니다.
Persistence Context에 persist() 하는 행위는 DB에 바로 저장하는 것이 아니라, persistence context에 영속시키는 것입니다.
우리 개발자들은 EntityManager를 통하여 이 persistence context에 접근할 수 있습니다.
EntityManager마다 Persistence Context 개념이 생성됩니다.
Entity Manager
종류
- Container Managed Entity Manager
- Servlet Container가 Entity Manager를 관리합니다. 즉, Container가 Entity Manager Factory를 사용하여 우리 대신 Entity Manager를 생성합니다.
- 트랜잭션의 시작, rollback, commit 모두 container가 관리합니다.
- 사용의 종료 시점에 entity manager를 close 하는 것 또한 container의 몫입니다. 우리가 직접 close하려 한다면 IllegalStateException이 나타납니다.
- Application Managed Entity Manager
- Container managed entity manager과는 다르게 우리가 entity manager factory를 사용하여 entity manager를 직접 생성해주어야 합니다.
- 트랜잭션의 시작, rollback, commit, close 등 모두 개발자의 몫입니다.
Thread Safe
Entity Manager Factory는 항상 thread-safe 합니다. 어디서 Entity Manager Factory 인스턴스를 불러와도 thread-safe 하게 사용할 수 있습니다.
그에 반해 Entity Manager는 thread-safe 하지 않습니다. Application managed 레벨에서는 thread-safe를 구현하는데 크게 어려움이 없습니다.
그러나 Container managed 레벨에서는 조금 미심쩍어 보입니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
@Service
public class someService{
@PersistenceContext
EntityManager entityManager;
// some business logic methods...
}
위와 같이 EntityManager를 주입한다면 모든 로직들이 같은 entityManager를 사용할 것만 같습니다. 그러나 실제로는 Container가 EntityManager 대신 특별한 Proxy를 주입합니다. Spring을 예로들자면, SharedEntityManagerCreator를 주입합니다.
우리가 주입된 entityManager를 사용할 때마다 이 프록시는 이미 존재하는 entityManager를 재사용하거나, 새로운 entityManager를 생성합니다.
Entity LifeCycle
- new / transient
- 새로 생성한 객체가 DB에도, persistence context에도 존재하지 않는 경우 new / transient 한 상태입니다.
- persist() 하지 않는 이상 DB에는 저장될 일이 없습니다.
- managed
- new / transient entity를 persist() 할 경우 managed 상태가 됩니다. 이후, persistence context에 적재되며, persistence context에게서 모든 관리를 받을 것입니다.
- flush()가 호출 되면 EntityManager에 의해 Dirty Checking이 적용되어 entity들의 수정사항이 자동으로 적용됩니다.
- detatched
- 더이상 managed 상태가 아닌 entity들 입니다. Persistence context의 관리를 받지 않는 상태이므로, 값이 수정되더라도 dirty checking이 이루어지지 않습니다.
- 그렇다고 detatched 된 데이터가 더이상 지속되지 않는 것은 아닙니다. 현재 세션과 분리된 상태입니다.
- 아래 예제를 통해 detached 되었다고 Persistence Context에서 해당 데이터가 제거되는 것은 아닌것을 확인할 수 있습니다. ``` java @Test @Transactional void detachedTest() { Vendor vendor1 = Vendor.builder() .name(“Super Cool Vendor”) .build();
vendorRepository.save(vendor);
vendorRepository.detach(vendor);
Vendor vendor2 = vendorRepository.findById(vendor.getId());
assertEquals(vendor2.getName(), “Super Cool Vendor”); Assertions.assertThat(vendor2).isNotEqualTo(vendor);
Vendor vendor3 = vendorRepository.findById(vendor.getId());
Assertions.assertThat(vendor3).isEqualTo(vendor2); } ```
- removed
Advantages of Persistence Context
-
1차 캐시
- 동일성 보장
- Repeatable read를 application 레벨에서 지원
- 쓰기 지연
- persist 마다 commit 하지 않고 1차 캐시에 insert query를 저장하고 있다 flush(), commit() 이 실행되면 그제서야 db에 저장
- jdbc batch option 가능
- @GeneratedValue(strategy = IDENTITY)인 경우에는 batch insert 불가
- insert 실행 후에 DB가 id를 정해주기 전까지는 모르기 때문
-
Dirty Checking
- Lazy Loading
예제
DB Schema
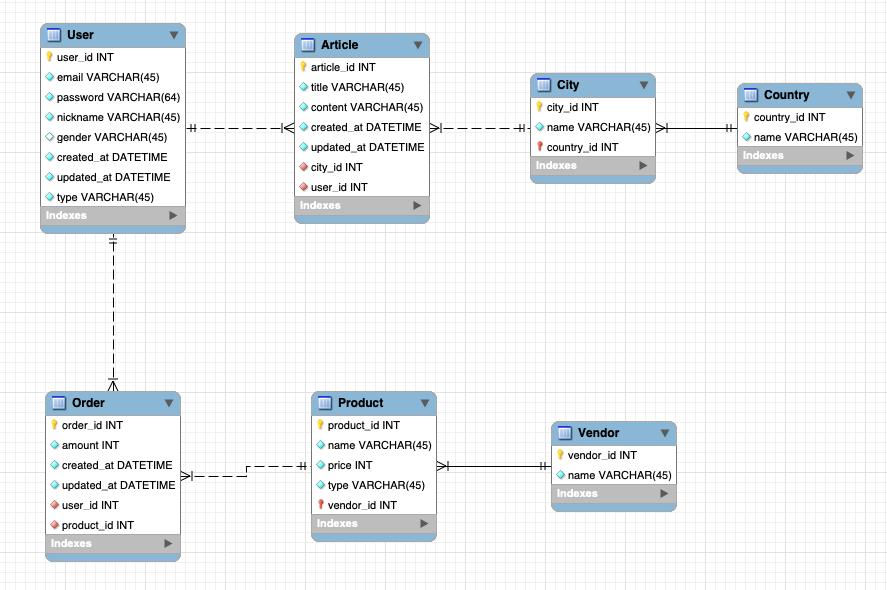

java faker를 사용하여 랜덤한 데이터를 삽입했습니다.
JPA Entity 작성
N + 1 문제
앞서, Entity의 relation mapping을 진행할 때, default를 EAGER LOADING으로 가지는 OOOToOne 관계들을 모두 LAZY LOADING으로 수정했었습니다. 간단한 테스트 코드를 작성하여 원하는 대로 단 한개의 쿼리를 사용하는지 확인해보았습니다.
Session 당 몇개의 query를 사용했는지 확인하는 법
properties, yml, xml 중 사용하는 설정 파일에 아래 항목을 추가해주면 됩니다.
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.generate_statistics=true
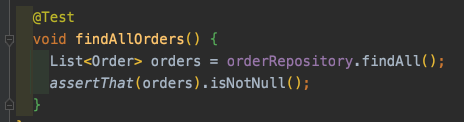
아래의 결과를 확인해보면 원하는 대로 쿼리를 한개 사용했음을 볼 수 있습니다.
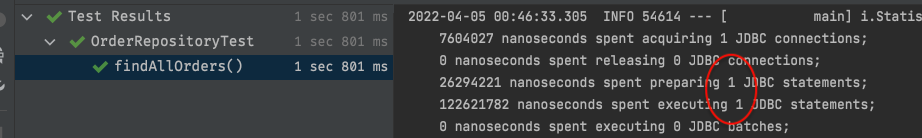
그렇다면 LAZY LOADING에서 EAGER LOADING으로 변경한다면 몇개의 쿼리나 사용할까요?
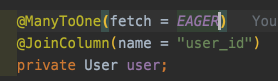
아래와 같이 Order Entity의 User 컬럼의 fetch type을 EAGER로 수정했습니다.
동일한 테스트 코드를 실행했을 때 결과는 아래와 같았습니다.
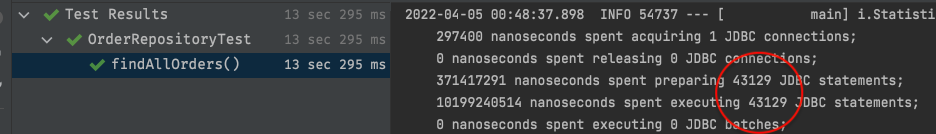
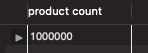
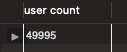
그런데 db에서 user의 전체 수를 확인해보면 아래와 같이 약 4만 9천 9백 9십 5명이 있습니다. 하지만 사용한 쿼리는 그와 동일한 49995건이 아닌 43129건 뿐이었습니다.

이유는 랜덤하게 데이터를 넣으면서 Order과 mapping 된 User의 수는 43128 명 뿐이기 때문입니다.
1
2
select count(distinct user_id)
from `Order`;
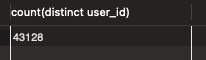
여기서 정확하게 N + 1 Problem이 발생한 것을 확인할 수 있었습니다.
Order 전체를 불러오는 데 사용한 한개의 쿼리 + 그 Order 당 mapping 된 User(43128)를 EAGER 하게 로딩하므로
총 43129개의 쿼리가 실행된 것입니다.
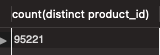
Order에 mapping 된 다른 엔티티인 Product도 동일하게 확인해보겠습니다.
아래와 같이 Product를 Eager하게 로딩하도록 설정하고,

위와 동일한 테스트 코드를 실행해보면, 아래와 같은 결과가 나타났습니다.
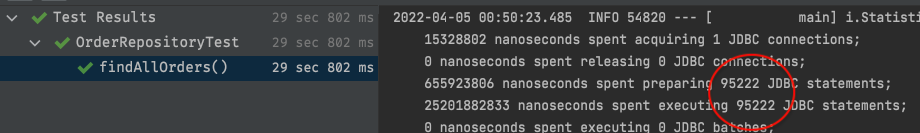
역시 랜덤한 데이터로 관계를 맺어주었기 때문에 정확히 N + 1 개의 쿼리가 실행된 것임을 확인할 수 있었습니다.
댓글남기기